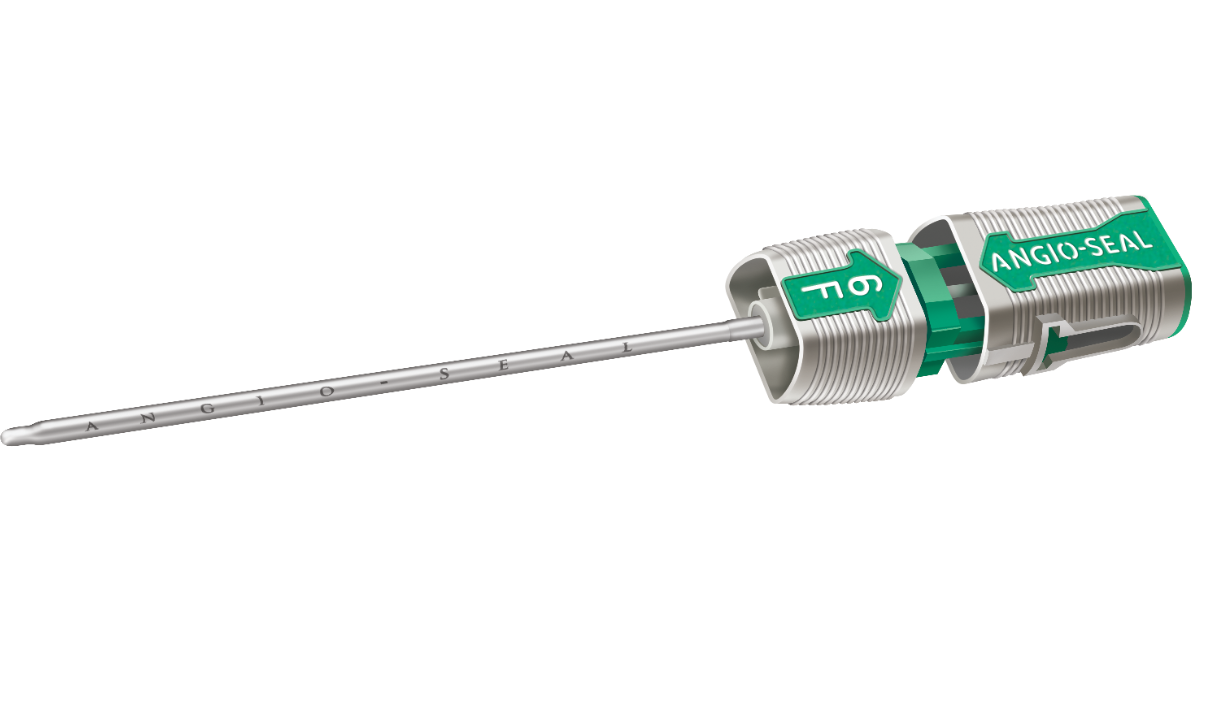
Angio-Seal® VIP Vascular Closure Device
Active closure for rapid and reliable hemostasis proven to accelerate patient mobility and enable same-day discharge2⁻7
- Resorbable components provide safe, effective and rapid closure8,9
- Lower bleeding complication rates compared to other hemostasis strategies10-13
- Manual compression not required for reinforcement of the closure14
BIOABSORBABLE COMPONENTS
- The device creates a mechanical seal by sandwiching the arteriotomy between a bioabsorbable anchor and collagen sponge, which dissolve in 60 to 90 days.8
Three bioabsorbable components actively seal the arteriotomy:
1. Anchor: Bioabsorbable co-polymer anchor placed against the inside of the vessel wall
2. Collagen: Placed on top of the arteriotomy in the tissue tract
3. Suture: Cinches the anchor and collagen together to form a secure seal

DOCUMENTS
REFERENCES
RX ONLY. Refer to the product labels and package insert for complete warnings, precautions, potential complications, and instructions for use.
- Data on file.
- Manolis AS, Georgiopoulos G, Stalikas D, Koulouris S. Simplified swift and safe vascular closure device deployment without a local arteriogram: Single center experience in 2074 consecutive patients. Indian Heart J. 2016 Jul-Aug;68(4):529-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2015.11.036. Epub 2016 Jan 11.
- Atonsen L, Jensen LO, Thayssen P. Outcome and safety of same-day-discharge percutaneous coronary interventions with femoral access: A single center experience. Am Heart J 2013; 165:393-9.
- Applegate RJ, Turi Z, Sachdev N, Ahmed A, Szyniszewski A, Foster M, Pratsos A, Shapiro T, Yakubov S, Shavelle D. The Angio-Seal Evolution registry: outcomes of a novel automated Angio-Seal vascular closure device. J Invasive Cardiol. 2010 Sep;22(9):420-6.
- Abando A, Hood D, Weaver F, Katz S. The use of the Angioseal device for femoral artery closure. J Vasc Surg. 2004 Aug;40(2):287-90.
- Yee KM, Lazzam C, Richards J, Ross J, Seidelin PH. Same-day discharge after coronary stenting: a feasibility study using a hemostatic femoral puncture closure device. J Interv Cardiol. 2004 Oct;17(5):315-20.
- Kapadia SR, Raymond R, Knopf W, Jenkins S, Chapekis A, Ansel G, Rothbaum D, Kussmaul W, Teirstein P, Reisman M, Casale P, Oster L, Simpfendorfer C. The 6Fr Angio-Seal arterial closure device: results from a multimember prospective registry. Am J Cardiol. 2001 Mar 15;87(6):789-91, A8.
- Nash JE, Evans DG. (1999). The Angio‐Seal hemostatic puncture closure device. Concept and experimental results. Herz, 24(8), 597‐606. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf03044483.
- Wong HF, Lee CW, Chen YL, Wu YM, Weng HH, Wang YH, Liu HM. Prospective comparison of angio-seal versus manual compression for hemostasis after neurointerventional procedures under systemic heparinization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Feb;34(2):397-401. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3226. Epub 2012 Aug 2.
- Resnic FS, Majithia A, Marinac-Dabic D, Robbins S, Ssemaganda H, Hewitt K, Ponirakis A, Loyo-Berrios N, Moussa I, Drozda J, Normand SL, Matheny ME. Registry-Based Prospective, Active Surveillance of Medical-Device Safety. N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 9;376(6):526-535. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1516333. Epub 2017 Jan 25.Gregory D, Midodzi W, Pearce N. Complications with Angio-Seal™ vascular closure devices compared with manual compression after diagnostic cardiac catheterization and percutaneous coronary intervention. J Interv Cardiol. 2013 Dec;26(6):630-8.
- Gregory D, Midodzi W, Pearce N. Complications with Angio-Seal™ vascular closure devices compared with manual compression after diagnostic cardiac catheterization and percutaneous coronary intervention. J Interv Cardiol. 2013 Dec;26(6):630-8.
- Tavris DR, Wang Y, Jacobs S, Gallauresi B, Curtis J, Messenger J, Resnic FS, Fitzgerald S. Bleeding and vascular complications at the femoral access site following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): an evaluation of hemostasis strategies. J Invasive Cardiol. 2012 Jul;24(7):328-34. Arora N, Matheny ME, Sepke C, Resnic FS. A propensity analysis of the risk of vascular complications after cardiac catheterization procedures with the use of vascular closure devices Am Heart J. 2007 Apr; 153 (4): 606-11.
- Arora N, Matheny ME, Sepke C, Resnic FS. A propensity analysis of the risk of vascular complications after cardiac catheterization procedures with the use of vascular closure devices Am Heart J. 2007 Apr; 153 (4): 606-11.
- ANGIO-SEAL VIP Instructions for Use, ASIN0004 revision 2018-09-01.
Important Safety Information:
Possible adverse events for vascular closure devices include, but are not limited to: bleeding or hematoma, AV fistula or pseudoaneurysm, infection, allergic reaction, foreign body reaction, inflammation or edema. This device should only be used by a licensed physician (or other health care professional authorized by or under the direction of such physician) possessing adequate instruction in the use of the device, e.g., participation in an Angio-Seal physician instruction program or equivalent.